Everything you need to know about aluminum extrusion
Aluminum extrusions are an essential products of our homes, although many people do not even notice them. They are usually products for window or door systems, but the application does not stop there. Aluminum bars or aluminum ingot have countless applications in building and manufacturing industries, therefore the quality of each products must be impeccable.
Shunho metal solutions is a big China supplier of aluminum extruded products. In our aluminum extrusion manufacturing process which is trusted by our customers in the world. We apply the best possible production practices which we continuously improve.

Aluminum profiles is transferred into hardening process in batches
Aluminum Extrusion Basics:
Extrusion process is a modern process in which aluminum extrusion are heated and pushed through a shaped die opening. The opening can be modified to create different shapes and sizes to fulfill our customer’s specific needs. Depending on the required aluminum extrusion type, we use different steel dies.
You can read more about the differences in the extrusion process and the created aluminum extrusion products on our website: https://www.shunhogroup.com.hk/
The 6 Steps for Aluminum Extrusion
The extrusion process is carried out in direct, indirect or Conform continuous extrusion presses with different power levels .The basic process can be broken down into six distinct steps, although they can be modified or expanded upon depending on the customer’s specific requirements.
But even before the extrusion process begins, the casting aluminum rods needs to be cut into smaller pieces. These short pieces are called aluminum billets. The pre-cut billets ensure that the length of each extruded bar will be roughly the same, in that way, there will be no material wastage.

Aluminium pig

Raw material aluminum ingot
Step 1: Preheating the aluminum billet and steel die to a specified temperature
The aluminum billets are heated in induction or gas furnaces from room temperature to the extrusion. The temperature varies depending on the aluminum alloy and the final temper.
The heated aluminum billets need to be malleable enough to take on the required shape, but still firm enough to retain their shape during transportation.
The push bat starts applying pressure into the heated aluminum billet and pushes it towards the die opening.
Step 2: Loading the aluminum billet into the steel extrusion press container
To prevent heat loss, the aluminum billets are quickly transported from the furnace into the press. They are loaded into the recipient and are ready to be extruded.
The ram starts applying pressure into the heated aluminum billet and pushes it towards the die opening.

Aluminum bars
The heated aluminum billet is pushed through the openings in the extrusion tooling . Those openings can be modified to create different shapes and sizes. The process is similar to a cookie press, where the different shaped discs create different cookie designs.
When the aluminum bars exit the press, they are already extruded to their required shape.

Aluminum extrusion
Step 4: Controlled cooling
The extrusion process is followed by quick cooling of the extruded aluminum bars/tubes/profile
When exiting the press, the fully formed bars/profiles are pushed through a water bath which guarantees uniform quenching of the heated aluminum.
The quenching process is necessary to ensure the required mechanical properties and adequate material microstructure.
To prevent any aluminum material deformation, the cooling process must be carried out without delays immediately after the extrusion process.
Immediately after quenching, the extruded aluminum bars are cut into the prescribed interphase length.
The cut bars are then grabbed by a puller, which lays them over the runout table. This allows them to further cool down.
In this phase, the extruded bars are run through a strengthening process, which stretches the aluminum bars and ensures their mechanical properties by removing the internal tension within the bars.

Aluminum bar cutting
Step 6: Cutting and final packaging
The quenched and straightened bars are cut to the length specified by the customer.
At this stage, the aluminum bars have the properties of the T1/T4 temper. To ensure better mechanical properties of the T5/T6/T66 temper, the bars are artificially aged.
The aging process further strengthens the extruded profiles and ensures they fulfill the mechanical properties specified for individual alloys.
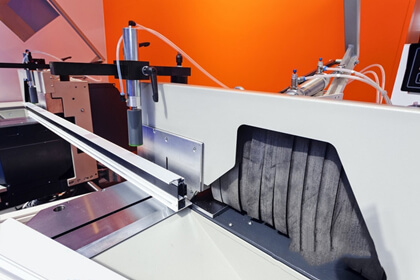
Aluminum profile cutting

Packaging for aluminun profile
What Factors Affect The Aluminum Extrusion?
While the above mentioned steps of the extrusion process may seem fairly simple, they are anything but. In truth, aluminum extrusion is a very complex process which is dependent on the correlation between numerous parameters that need to be adapted during extrusion process. Those parameters are called TST parameters and refer to the temperature, speed and time.
In essence, before, during and after extrusion, the following factors must be closely monitored:
Aluminum Billet temperature in heating furnaces
Container temperature
Extrusion tooling temperature
Exit temperature of the aluminum bar or profile
Quench media temperature
Extrusion rate and quench delay
Extrusion speed
Final products and extrusion tool dimensions
These parameters must be closely controlled and monitored. The most important among them is temperature, which needs to be adapted depending on the extruded aluminum material and the desired final shape of the aluminum products. In general, the aluminum alloy billets need to be heated to between 300 and 595°C.
Another very important products of the extrusion process is quenching. As talked above, the extruded aluminum profiles are quenched immediately after exiting the die. In this stage it is essential that every product of the aluminum bar is covered by the right amount of water for the right amount of time. It means that they cool down from the extrusion temperature to room temperature as quickly as possible. Only then can the extruded bars, tubes and profiles be cooled uniformly and reach the highest mechanical and technological properties. The fastest quenching rate will achieve the best combination of strength, toughness and microstructure. This process is commonly be used in producing extruded shapes of the 6xxx Al series e.g the T66 temper, such as AL6063-T5 we always use for customers.

Aluminium extrusion for heat sinks
After the extrusion and quenching process is completed successfully, the following parameters need to be monitored closely:
Dimensions and tolerances of the aluminum products
Surface finish on the aluminum products.
Mechanical properties
Macrostructure of the bars, profiles and tubes (without back end defects)
Other special quality considerations

Aluminum profile products
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion Process
In comparison to other products, aluminum extrusions are the preferential option due to their unique combination of lightness and toughness. From the industry viewpoint, aluminum extrusion has additional advantages as below:
They are generally a competitive and economical production option especially when dealing with very complex cross-sections.
They are stronger and tough
The surface finish of extruded aluminum products is impeccable and in general, those kind of aluminum products are stronger when compared to aluminum die castings.
Despite the numerous advantages mentioned above, there is also an important disadvantage to aluminum extrusions in comparison to die casting. And that is their size. Aluminum extrusions are limited by the size of both the billet and the capacity of the steel container on the extrusion press.
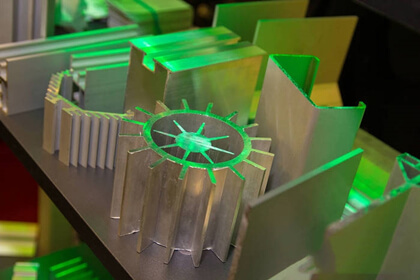
Aluminum extrusion products
Different Extrusion Types you can choose
In extrusion process, there are three different extrusion processes:
Direct extrusion is the simplest production mode for us. This method is most commonly used to produce aluminum extrusions. In it, the die is stationary while the ram forces the billet through the die opening. The action of the billet and ram moving forward in the same direction has led to this method being called the forward or direct aluminum extrusion process.
Indirect extrusion is a process in which the billet remains stationary, but the assembly on the end of the ram moves against the aluminum billet. This creates the extrusion pressure necessary for metal to flow through the die.
This is the main advantage of the indirect press as it enables the pressing of harder alloys and products with smaller cross-sections due to the smaller extrusion pressures. Lower pressures also allow for lower pressing temperatures and consequently greater extrusion speed. This of course increases productivity.
Conform continuous extrusion
Conform continuous extrusion. A common feature of the various methods mentioned above is the discontinuity of extrusion production. A series of auxiliary operations such as separation of excess pressure and filling of blanks are required between the extrusion of the front and rear billets, which affects the efficiency of extrusion production and is not conducive to the extrusion process.
Do you know what Shapes can be extruded?
Extrusion is a product of so many industries that it is not possible to create a complete list of every one of its types. There are limitless possibilities regarding shapes which are available in a wide range of configurations and sizes. The main categories are listed belw:
Solid shapes: Solid aluminum bars and rods with various cross-sections (e.g. circles, rectangles, squares, etc.)
Semi-solid shapes: such as angles, channels, and other partially open forms
Hollow shapes: Aluminum tubes or profiles with various cross-sections (e.g. circles, rectangles, squares, etc.)
Extruded as a semi-finished products
Especially in large and complex industries, the extruded bars are sometimes not suitable to be used as finished products due to their wider tolerances, worse straightness and greater surface roughness. For such demanding industries, drawn products are more suitable, as the tolerances are significantly more rigorous and the surface is smoother. Drawn products allow customers to achieve greater productivity, less work operations and a smaller scrap share.
In comparison to aluminum extrusion, drawing is a cold manufacturing process that forms aluminum bars by reducing their cross-section. This is accomplished by pulling the bar and tube through a smaller die. Although the process is similar to aluminum extrusion, the direction of the applied force is different.
The drawing process has many important factors that affect the quality and precision of formed bars or tubes, such as die angle, drawing speed, lubrication condition and pass reduction ratio.
For cases of extremely complex final aluminum products or thinner aluminum products you are going to use, the extruded products are replaced by rolled parts or by mechanical processing (Like CNC machining) or forging simpler extruded aluminum products (flat, square or hexagonal bar). This is how we can ensure the aluminum products of more challenging shapes or with more precise dimensions.
If you have any additional questions about our services or processes, you can visit our website for more information or contact us sales@shunhogroup.com.hk

2D inspection for aluminum extrusion heatsink

Aluminum profile inspection

Aluminum profiles for Windows, doors, and bathroom boxes

Polishing for aluminum extrusion products
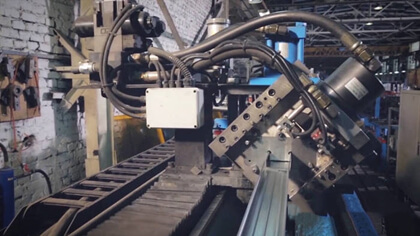
The engine of aluminum profile


















